What is SNMP ?
SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol) is the standard protocol for the Internet. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) developed it.
 SNMP is nothing more than a standard language that computers use to control each other and report important information. Its advantage today is that a very large number of devices support it, enabling them to work together.
SNMP is nothing more than a standard language that computers use to control each other and report important information. Its advantage today is that a very large number of devices support it, enabling them to work together.
SNMP is used to manage network devices that span(monitor) firewalls or embedded devices. SNMP is mainly used in network management systems to monitor network-attached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention.
How long has it been around ?
SNMP was created in 1988. At the time, it was simply a short-term way to manage computers on the Internet and in private networks. It replaced the earlier "SGMP" ("G" stood for for "Gateway").
Now, of course, SNMP is just about everywhere. You'll find it in corporate office buildings, remote industrial telecom sites, and even home offices.
How do the pieces fit together ?
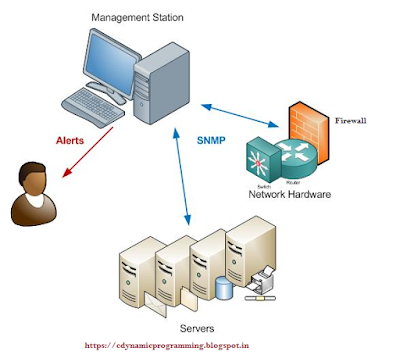
SNMP architecture is, in principal, very similar to the internet technology you're using right now to read this web page. Your computer (or tablet, or smartphone) sends a standardized request to our web server. So do other computers around the world. Our web server responds by sending each of you the information you want. There are many computers in various locations, and our single server sends web pages to all of them.
In SNMP, "agents" are remote devices out in the network. What exacty the agents are depend on the kind of network you have (ex. Are you a small office, a national telephone company, or a power utility?). They can be printers, managed switches, alarm remotes, generators, servers, and lots of other things. These agents report problems and receive commands from a central "manager". This is known, oddly enough, as the "manager-agent model".
SNMP is a simple request/response protocol that communicates management information between two types of SNMP software entities: SNMP managers and SNMP agents.
SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol) is the standard protocol for the Internet. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) developed it.
 SNMP is nothing more than a standard language that computers use to control each other and report important information. Its advantage today is that a very large number of devices support it, enabling them to work together.
SNMP is nothing more than a standard language that computers use to control each other and report important information. Its advantage today is that a very large number of devices support it, enabling them to work together.SNMP is used to manage network devices that span(monitor) firewalls or embedded devices. SNMP is mainly used in network management systems to monitor network-attached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention.
How long has it been around ?
SNMP was created in 1988. At the time, it was simply a short-term way to manage computers on the Internet and in private networks. It replaced the earlier "SGMP" ("G" stood for for "Gateway").
Now, of course, SNMP is just about everywhere. You'll find it in corporate office buildings, remote industrial telecom sites, and even home offices.
How do the pieces fit together ?
SNMP architecture is, in principal, very similar to the internet technology you're using right now to read this web page. Your computer (or tablet, or smartphone) sends a standardized request to our web server. So do other computers around the world. Our web server responds by sending each of you the information you want. There are many computers in various locations, and our single server sends web pages to all of them.
In SNMP, "agents" are remote devices out in the network. What exacty the agents are depend on the kind of network you have (ex. Are you a small office, a national telephone company, or a power utility?). They can be printers, managed switches, alarm remotes, generators, servers, and lots of other things. These agents report problems and receive commands from a central "manager". This is known, oddly enough, as the "manager-agent model".
SNMP is a simple request/response protocol that communicates management information between two types of SNMP software entities: SNMP managers and SNMP agents.
In summary, the SNMP Management program performs the following operations:
- The GET operation receives a specific value about a managed object, such as the available hard disk space from the agent's MIB.
- The GET-NEXT operation returns the "next" value by traversing the MIB tree of managed object variables.
- The SET operation changes the value of a managed object's variable. Only variables whose object definition allows read/write access can be changed.
- The TRAP operation sends a message to the Management Station when a change occurs in a managed object, and that change is important enough to send an alert message.
What versions of SNMP are available ?
There are several SNMP versions, including v1, v2, and v3.
The SNMP v1 network management architecture contains:
There are several SNMP versions, including v1, v2, and v3.
The SNMP v1 network management architecture contains:
- Network Management Station (NMS) - Workstation that hosts the network management app.
- SNMPv1 network management application - Polls management agents for information and provides control info to agents.
- SNMPv1 management agent(s) - Provides info contained in the MIB to management applications and may accept control information.
- SNMP v2 specs include the following new capabilities:
The management station is simply software that collects information from your network. Most management stations will poll your network for information regularly. Management stations range from the very simple to highly complex.
Manager to manager communication to support multiple / distributed managers and mid-level managers.
Better security (known as "Secure SNMP") by specifying three layers of security.
Improved efficiency and performance through the addition of bulk transfers of data.
SNMP v3 specs include the encryption required by security-conscious organizations.
Better security (known as "Secure SNMP") by specifying three layers of security.
Improved efficiency and performance through the addition of bulk transfers of data.
SNMP v3 specs include the encryption required by security-conscious organizations.
 What is MIB ?
What is MIB ?Each station or agent in an SNMP-managed network maintains a local database of info relevant to network management. This is known as the management information base (MIB).
The MIB is a type of database used to manage the devices in a network. It is a group of objects in a (virtual) database used to manage gear such as routers in a network.
In short, MIB files are the set of questions that a SNMP Manager can ask the agent. Agent collects these data locally and stores it, as defined in the MIB. So, the SNMP Manager should be aware of these standard and private questions for every type of agent.
What Is an SNMP-Compliant MIB (SNMP) ?
A management station gets and sets objects in the MIB, and an agent notifies the management station of major but unwanted events called traps. All message exchanges between the management station and its agents take place using SNMP. The MIB at the management station contains network management info taken from the MIBs of all the managed parts in the network.
Why do I need the MIB ?
Your SNMP manager needs the MIB in order to process messages from your devices. The MIB is also your best guide to the real capabilities of an SNMP device. You need to be able to read the MIB so that you can have a good idea of what assets you do have.
What is Private MIB ?
SNMP allows the extension of snmp standard values with values specific to a particular agent through the use of private MIBs.
How do I look at a MIB ?
One of the best tactics for addressing MIB problems is to simply read through the file. As a MIB (SNMP) file is just ASCII text, you can view it in any word processor or text editor (even Notepad). Some manufacturers provide grouped MIBs in binary format, but those aren't readable. You want the raw ASCII version of the MIB (SNMP) file.
- An MIB (SNMP) contains definitions and info about the properties of managed resources and the services that the agents support.
- It also contains standard set of statistical and control values defined for hardware nodes on a network.
A management station gets and sets objects in the MIB, and an agent notifies the management station of major but unwanted events called traps. All message exchanges between the management station and its agents take place using SNMP. The MIB at the management station contains network management info taken from the MIBs of all the managed parts in the network.
Why do I need the MIB ?
Your SNMP manager needs the MIB in order to process messages from your devices. The MIB is also your best guide to the real capabilities of an SNMP device. You need to be able to read the MIB so that you can have a good idea of what assets you do have.
What is Private MIB ?
SNMP allows the extension of snmp standard values with values specific to a particular agent through the use of private MIBs.
How do I look at a MIB ?
One of the best tactics for addressing MIB problems is to simply read through the file. As a MIB (SNMP) file is just ASCII text, you can view it in any word processor or text editor (even Notepad). Some manufacturers provide grouped MIBs in binary format, but those aren't readable. You want the raw ASCII version of the MIB (SNMP) file.

Excellent blog! The information shared in this blog content about network management is really very helpful and informative. Thanks for sharing with us. Please share more such information in future. All the best!
ReplyDeleteNetwork Management Services USA
your article is nice and informative network and it suport system their services are best,if you need contact them.
ReplyDeleteNice article IT Managed Services.
ReplyDeletewonderful article keep it up
ReplyDeleteNetwork Device Kya Hai?
Motherboard Kya Hai?
Proxy Server Kya Hai?
Linux Kya Hai?
Thanks for sharing this useful information regard
ReplyDeleteVisit link
Best Hospital Management Software in India
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing this information. It will help the learners alot.
managed it support
remote access solution
Thank you for sharing the information
ReplyDeleteUsing Monitoring Services to Ensure Network Resilience | TechTriad
A Very Nice Blog, Very Informative. Safeguard Your Future: Leading Risk Services | FYI Solutions
ReplyDeleteNice Blog, Very Informative. Expert Software Testing Services - Ensure Quality | FYI Solutions
ReplyDeleteThank you for sharing informative blog Network Monitoring Services
ReplyDeleteCool
ReplyDelete